What Is A Yield Curve, And What Information Would You Need To Draw This Curve?
Past Saumen Chattopadhyay, CFA®, Senior Vice President, Investment Platform
If you've paid attention to market prognostications over the last year, you've likely heard the term "yield bend." The yield bend has get the centre of attending for explaining the economy and markets, which is why our financial advisors always seem to be answering one question: What is the yield curve?
The yield curve is the visual representation of interest rates and different maturities of fixed income securities. The "curve" of this graph shows u.s.a. how these rates trend currently and are expected to proceed.
What Makes Upwards the Yield Curve
A stock-still income security , commonly known equally bond, is a loan that the bondholder makes to the bond issuer. As with every loan, a bond pays interest periodically and repays the principal at the stop of the loan term, known equally maturity.
Short-term involvement rates worldwide are administered by nations' central banks . In the United States, the Federal Reserve (the Fed) conducts monetary policy and sets the federal funds rate , the criterion for other brusk-term interest rates.
The Federal Reserve Board's Open Market Committee (FOMC) raises and lowers the Fed funds rate that influences the overall supply of coin and credit in the economy. The FOMC sets a target, which is known as the constructive federal funds rate (FFR). This is the benchmark interest charge per unit used by banks and other depository institutions for the overnight borrowing and lending to meet brusk-term business organisation needs.
What Makes the Bend Happen
The shape of the yield curve depends primarily on two factors:
- Maturity Run a risk Premium : Investors expect actress returns for the added risk of holding bonds for a longer period of time. These added returns are chosen maturity risk premiums.
- Term Premium : The expectation most future economical growth, inflation and monetary policy is called term premium.
Demand for money is higher when the economy is growing because dandy spending activity demands higher funds to finance projects. High demand, in plough, drives up interest rates. Higher inflation is usually caused past potent economical growth.
Thus, in periods of economic expansion, investors expect the bond yields with longer-maturity to be higher than shorter-term because they look future higher interest rates likewise as inflation. This difference between short-term and long-term rates is known as "the spread." Higher spread gives an upward sloping yield curve.
A Steep Yield Curve
A steep yield curve is typically a positive sign for the economy, meaning that investors expect higher interest rates and inflation. It indicates investors are confident about putting money into stocks and individual sector bonds, therefore long-term government bonds take to offer higher yields to attract buyers.
In mid-February 2022, the curt-term, 2-year involvement rate was 0.29% while the10-year involvement charge per unit was 2.05%. That 1.76% difference in interest compensated the investor for investing over a longer period of time. Beneath was the upward sloping yield curve from mid-February 2022.
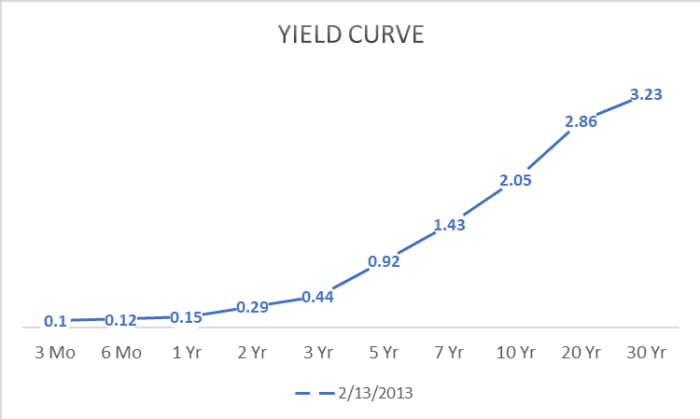
Source information: Treasury.gov
On the other paw, slower economic growth reduces the demand for money when businesses are less likely to produce more than or finance projects with loans. Lower demand for loans puts downwards pressure on involvement rates.
Also, during weaker economic growth, the Fed is more likely to reduce short-term interest rates to encourage people to borrow and spend. For example, the FOMC lowered its target for the federal funds rate to nigh aught at the cease of 2008 to support the economy during fiscal crunch.
A Flat Yield Curve
A apartment yield bend indicates that fiddling if any difference exists between short-term and long-term rates for bonds and notes of similar quality . Flat curves often indicate the economy is slowing downwardly and investors are uncertain near the futurity path of the economy, including aggregate demands, inflation and the futurity value of stocks and bonds.
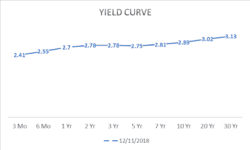
In December 2022, the curt-term, 2-year interest rate was ii.78%, while the10-yr interest rate was 2.89%. That 0.eleven% difference in interest compensates the investor for investing over a longer catamenia of time, simply it isn't much different than the short-term rate, therefore information technology'south called "flat." Beneath was the flat yield curve from December 2022.
Source data: Treasury.gov
An Inverted Yield Curve
An inverted yield curve happens when due south hort-term interest rates are higher than long-term rates . This seems similar a paradox at first glance – why would investors settle for lower yields property longer maturity compared to shorter-term? This is because they look the future rates to be even lower, every bit they have piffling to no faith in the economic system going forward. A negative term spread (typically, the difference betwixt 10-year and 2-year yield) evidently predicts weaker economic growth in the future with a loftier probability of recession.
Economic research shows the yield curve was inverted (measured in terms of the difference between 10-yr and 1-year treasury yields) prior to every recession from Jan 1955 to Feb 2022.
Although inversion of the yield bend is considered a harbinger of a recession, the inversion alone does non necessarily indicate an impending recession. Just the longer the yield curve stays inverted, the better information technology predicts recession, especially in the United States, when it'southward associated with a rising effective federal fund rates (FFR).
If you go in for such omens equally the Super Bowl indicator , the inverted yield curve is basically an AFC win, and they've been collecting rings for quite a few years now.
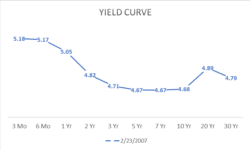
In February 2007, the short-term two-twelvemonth involvement rate was 4.82%, while the 10-year involvement rate was four.68%. That -0.14% divergence in interest compensates the investor for investing over a longer menses of fourth dimension, and thus the short-term was less than the long-term. Below was the inverted yield curve from March 2007.
Source data: Treasury.gov
How to Read the Bend
Although the shape of the yield bend shows expectations of interest rates and economic activity, it is important to distinguish the drivers of the short finish and long stop of the curve.
The curt-term interest rates are a function of the Fed FOMC'south budgetary policy deportment with its target federal funds charge per unit. The Fed FOMC "eases" by lowering the target rate and "tightens" past increasing the target charge per unit. On the other mitt, the changes in higher yields on longer-term maturity can indicate futurity economic growth and aggrandizement.
The yield curve is often considered a leading indicator for the management of an economy. Nonetheless, information technology's important to retrieve that there are some inherent limitations on what investors can acquire from just looking at the yield bend.
Employ the yield bend as a resources forth with your fiscal advisor , but don't rely on i unmarried data point in your controlling process. Your counselor should be able to help guide you with all the information at his or her disposal.
Schedule an appointment with a Carson Wealth advisor today to get started edifice your programme.
Source: https://www.carsonwealth.com/insights/blog/what-is-the-yield-curve-and-what-does-it-tell-us/
Posted by: cundiffthaveling73.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Yield Curve, And What Information Would You Need To Draw This Curve?"
Post a Comment